
Line HD can have a positive or negative slope depending on whether the liquid expands or contracts on freezing. Ice water at 0☌ and atmospheric pressure occurs on this line. Line HD is the equilibrium line between solid and liquid. The use of "dry ice" for cooling is an example of this. Point H, the triple point, is the only combination of pressure and temperature at which all three phases can exist together.Īlong line FH no liquid phase is ever present and solid sublimes to vapor. At equilibrium, one can change phase, by simply adding or removing energy from the system. Lines HD, HC, and FH are the equilibrium lines - combinations of pressure and temperature at which the adjoining phases are in equilibrium. Depending on the component’s pressure and temperature, it may exist as a vapor, a liquid, or some equilibrium combination of vapor and liquidįigure 2-1 P-T Diagram for pure component. Intermediate-weight hydrocarbons may condense from rich gases upon cooling.Ī pure component of a natural gas system exhibits a characteristic phase behavior, as shown in Fig.
Lean gases burn with a low air-to-gas ratio and display a colorless to blue or yellow flame, whereas rich gases require comparatively higher amounts of air for combustion and burn with an orange flame. In addition, operators may intentionally add odorants, tracers (such as helium), or other components.ĭry, or lean, natural gas systems have high concentrations of the lighter hydrocarbons (methane and ethane), while wet, or rich, gas systems have higher concentrations of the intermediate-weight hydrocarbons. These constituents may occur naturally in gas reservoirs, or they may enter the system as contaminants during production, processing, and transportation.

Natural gas systems can also contain non-hydrocarbon constituents, including hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor. These components are commonly referred to as pentanes-plus, condensate, natural gasoline, and natural gas liquids (NGL). The intermediate-weight hydrocarbons (pentane through decane) exist as volatile liquids at atmospheric conditions. These are the primary components of liquefied petroleum gas, or LPG. Propane (C3H8), butane (n-C4H10 and i-C4H10), and heavier hydrocarbons may be extracted from the gas system and liquefied for transportation and storage. Methane and ethane exist as gases at atmospheric conditions.
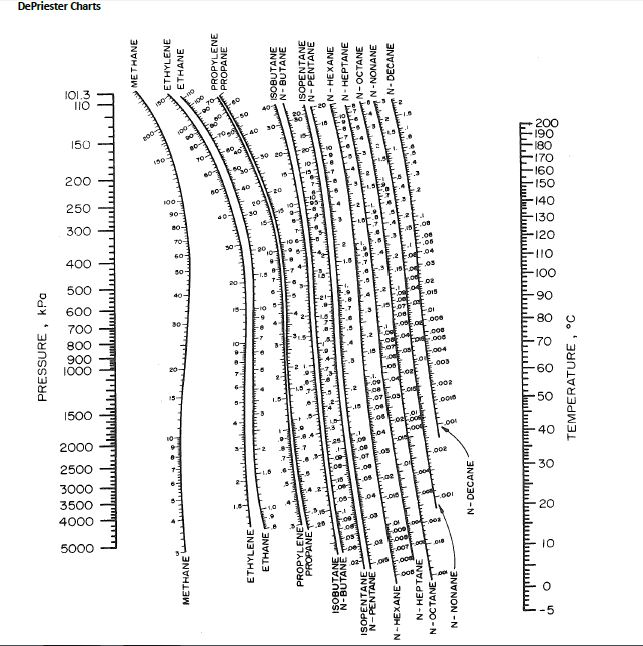
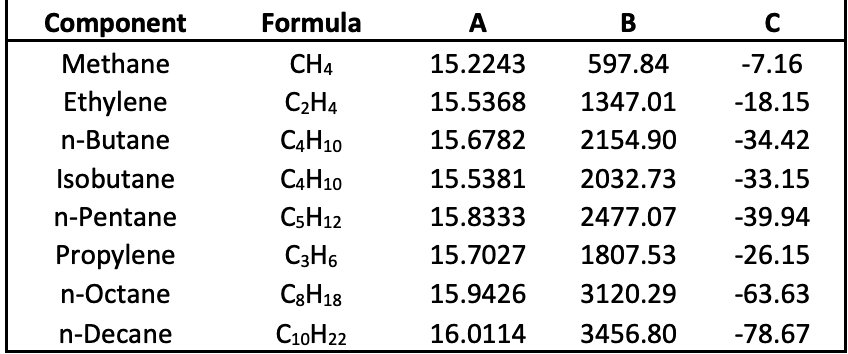
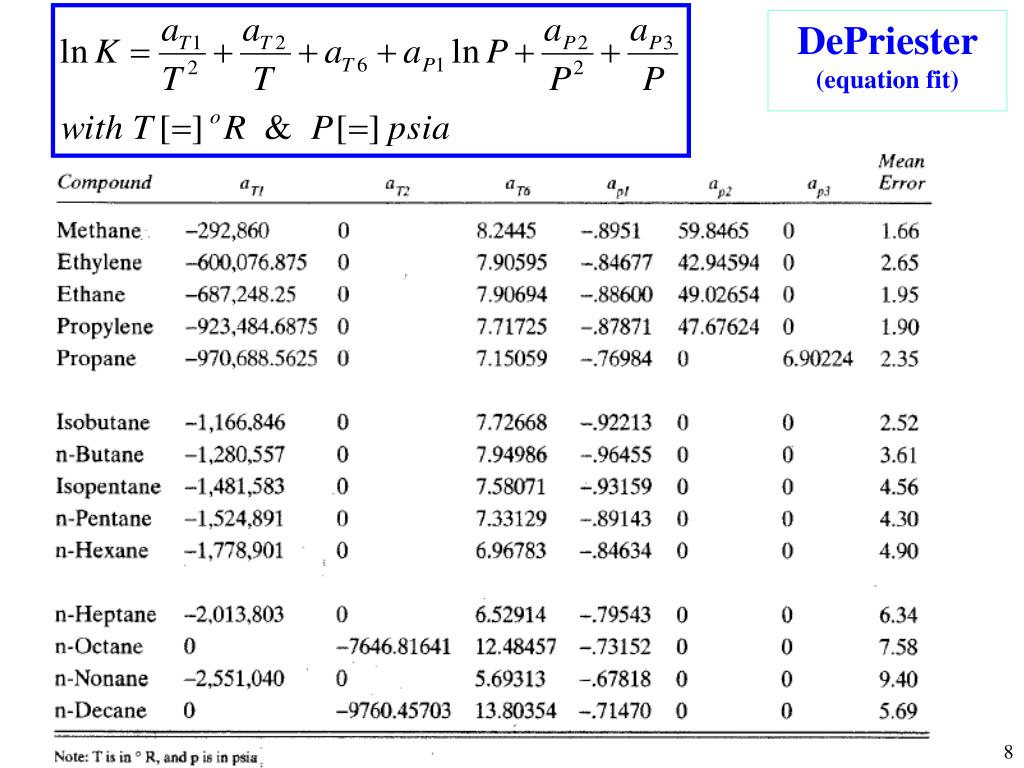
HYDROCARBON DEPRIESTER CHART SERIES
Natural gas systems are composed primarily of the lighter alkane series of hydrocarbons, with methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6) comprising 80% to 90% of the volume of a typical mixture. Phase diagrams illustrate the phase that a particular substance will take under specified conditions of pressure, temperature, and volume.
Phase defines any homogeneous and physically distinct part of a system that is separated from other parts of the system by definite bounding surfaces: Prediction and Inhibition of Gas Hydrates Bookīasics of Corrosion in Oil and Gas Industry Bookīefore studying the separation of gases and liquids, we need to understand the relationship between the phases. Fundamentals of Oil and Gas Processing Book


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
